| |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
A.3.12 Algebraic dependence
Let
![]() ,
, ![]() , ...,
, ...,
![]() .We want to check whether
.We want to check whether
-
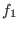 , ...,
, ..., 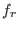 are algebraically dependent.
are algebraically dependent.
Let
![$I=\langle Y_1-f_1,\ldots,Y_r-f_r \rangle \subseteq
K[x_1,\ldots,x_n,Y_1,\ldots,Y_r]$](sing_484.png) .Then
.Then
![$I \cap K[Y_1,\ldots,Y_r]$](sing_485.png) are the algebraic relations between
are the algebraic relations between
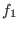 , ...,
, ..., 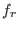 .
. -
![$g \in K [f_1,\ldots,f_r]$](sing_486.png) .
.![$g \in K [f_1,\ldots,f_r]$](sing_486.png) if and only if the normal form of
if and only if the normal form of
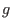 with respect to
with respect to
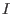 and a
block ordering with respect to
and a
block ordering with respect to
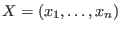 and
and
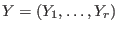 with
with 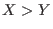 is in
is in
![$K[Y]$](sing_490.png) .
.
Both questions can be answered using the following procedure. If the second argument is zero, it checks for algebraic dependence and returns the ideal of relations between the generators of the given ideal. Otherwise it checks for subring membership and returns the normal form of the second argument with respect to the ideal I.
proc algebraicDep(ideal J, poly g)
{
def R=basering; // give a name to the basering
int n=size(J);
int k=nvars(R);
int i;
intvec v;
// construction of the new ring:
// construct a weight vector
v[n+k]=0; // gives a zero vector of length n+k
for(i=1;i<=k;i++)
{
v[i]=1;
}
string orde="(a("+string(v)+"),dp);";
string ri="ring Rhelp=("+charstr(R)+"),
("+varstr(R)+",Y(1.."+string(n)+")),"+orde;
// ring definition as a string
execute(ri); // execution of the string
// construction of the new ideal I=(J[1]-Y(1),...,J[n]-Y(n))
ideal I=imap(R,J);
for(i=1;i<=n;i++)
{
I[i]=I[i]-var(k+i);
}
poly g=imap(R,g);
if(g==0)
{
// construction of the ideal of relations by elimination
poly el=var(1);
for(i=2;i<=k;i++)
{
el=el*var(i);
}
ideal KK=eliminate(I,el);
keepring(Rhelp);
return(KK);
}
// reduction of g with respect to I
ideal KK=reduce(g,std(I));
keepring(Rhelp);
return(KK);
}
// applications of the procedure
ring r=0,(x,y,z),dp;
ideal i=xz,yz;
algebraicDep(i,0);
==> _[1]=0
// Note: after call of algebraicDep(), the basering is Rhelp.
setring r; kill Rhelp;
ideal j=xy+z2,z2+y2,x2y2-2xy3+y4;
algebraicDep(j,0);
==> _[1]=Y(1)^2-2*Y(1)*Y(2)+Y(2)^2-Y(3)
setring r; kill Rhelp;
poly g=y2z2-xz;
algebraicDep(i,g);
==> _[1]=Y(2)^2-Y(1)
// this shows that g is contained in i.
setring r; kill Rhelp;
algebraicDep(j,g);
==> _[1]=-z^4+z^2*Y(2)-x*z
// this shows that g is contained in j.
|