 |
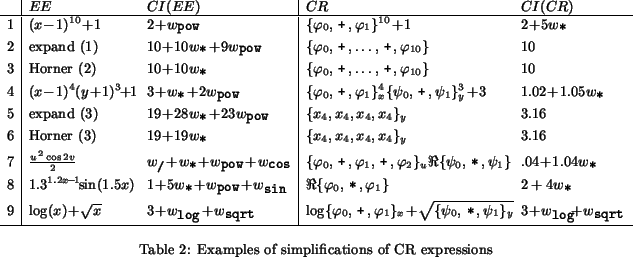
We conclude this section by illustrating the suggested heuristic
simplification procedures. In Table 3 we give
examples which are very similar to those used in [#!me:sigsam!#] to
measure and demosntrate the evaluation speed of our implementation of
the CR method.
We furthermore assumed that expressions of the form xn were always evaluated using the <tex2htmlverbmark>57<tex2htmlverbmark> operation for elementary expressions and using a repeated squaring procedure for CR expressions.
For row 2 we used the expanded form of
(x-1)10+1 as input, i.e.
![]() and for row 3 we
used the Horner representation of
(x-1)10+1 as input, i.e.
and for row 3 we
used the Horner representation of
(x-1)10+1 as input, i.e.
![]() .
Likewise, for rows
5 and 6, we used the expanded input
.
Likewise, for rows
5 and 6, we used the expanded input
![]() and the Horner representation
and the Horner representation
![]() .
.
All CR expressions in column 3 are optimal, i.e., the heuristic simplification algorithm returned the same results as the exhaustive search algorithms. This illustrates that especially for relatively simple examples (like the ones above), the results of the heuristic simplification algorithm are usually as good as those from the exhaustive search algorithm (only much more efficient).
Notice also that the CR method does not result in a decrease of the CI for the example in row 9, i.e., the input expression does not allow CR simplifications.